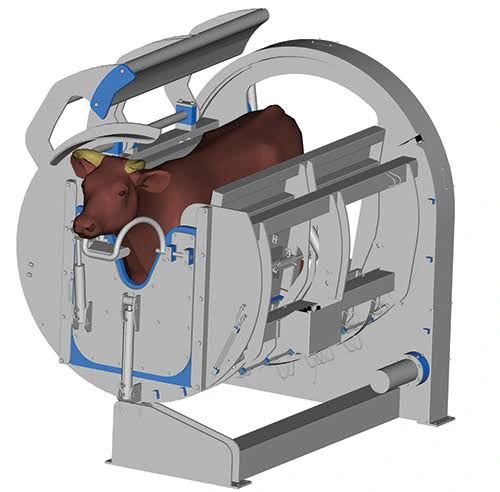
The meat industry relies on efficient and humane practices. Here’s a breakdown of two contrasting tools used in cattle slaughter house:
Practical Tool: Cattle Killing Box
- Function: This box safely restrains cattle during the slaughtering process.
- Benefits:
- Ensures safety for both workers and animals.
- Improves efficiency by allowing for a controlled environment.
- Contributes to humane handling.
- Link: For reference on a Cattle Killing Box, you can visit a website like MyCart.com.bd (Note: This link showcases a specific model, not a ritualistic pen).
Non-Essential Tool: Ritual Casting Pen
- Function: While not directly used in slaughtering, some cultures may use a designated pen to hold cattle before the slaughter.
- Focus: Primarily on religious or ritualistic practices.
- Alternatives: Modern slaughterhouses prioritize humane handling and efficiency. Restraint boxes fulfill this purpose.
Focus on Efficiency and Humane Practices
Modern slaughterhouses prioritize efficient and humane methods. The cattle killing box exemplifies this approach, ensuring both worker safety and animal welfare. While cultural and religious practices are important, the focus in slaughterhouses should be on following proper safety and animal handling protocols.
Why it’s used:
* Safety: Restraining the animal ensures the safety of both the animal and the workers.
* Efficiency: The controlled environment allows for a more efficient slaughtering process.
* Humane Handling: Proper restraint can minimize stress and pain for the animal.
Maintenance Guide:
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the safety and efficiency of the cattle restraint box. Here are some key maintenance tips:
Daily Maintenance:
* Visual Inspection: Check for any signs of damage, wear, or loose components.
* Cleanliness: Clean the box and its components to remove any blood, dirt, or other debris.
* Lubrication: Lubricate moving parts, such as hinges and hydraulic cylinders, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Weekly Maintenance:
* Hydraulic System: Check the hydraulic fluid level and pressure.
* Electrical Components: Inspect electrical wiring and controls for any damage or loose connections.
* Safety Devices: Ensure that safety devices, such as emergency stop buttons and pressure relief valves, are functioning correctly.
Monthly Maintenance:
* Thorough Cleaning: Perform a deep cleaning of the entire box, including hard-to-reach areas.
* Hydraulic Fluid Change: Change the hydraulic fluid as recommended by the manufacturer.
* Belt and Pulley Inspection: Check belts and pulleys for wear and tension.
Annual Maintenance:
* Professional Inspection: Have a qualified technician inspect the entire system, including the hydraulic system, electrical components, and mechanical parts.
* Calibration: Calibrate any sensors or gauges to ensure accurate readings.
* Replacement of Worn Parts: Replace any worn or damaged parts, such as hydraulic hoses, seals, or electrical components.
Additional Tips:
* Operator Training: Ensure that operators are properly trained on the safe and efficient use of the restraint box.
* Emergency Procedures: Have a well-defined emergency procedure in place to handle unexpected situations.
* Regular Servicing: Schedule regular maintenance and service intervals to keep the equipment in optimal condition. For service your Slaughter House can visit immenso.com.bd